Introduction
Have you ever wondered how the compact devices we use daily, like smartphones and laptops, manage to perform complex tasks so efficiently? How does a small chip inside these devices handle such heavy processing? What makes these electronic devices so powerful yet compact? The answer lies in the heart of these devices – the PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) and the tiny packages on them known as BGA (Ball Grid Array) packages.
Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages are integral components of modern electronics, enabling devices to be more compact and efficient. They are a type of surface-mount packaging used for integrated circuits, with various types each having unique features and applications. The choice of BGA package can significantly impact the design, performance, and cost of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) manufacturing, making them a key consideration in the electronics manufacturing process.
Understanding BGA Packages
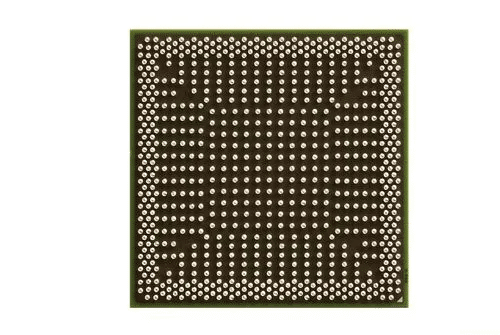
BGA packages, or Ball Grid Array packages, are a type of surface-mount device packaging used for integrated circuits (ICs). They are named for the grid-like pattern of solder balls on the underside of the package, which serve as the electrical connections between the IC and the PCB.
One of the key advantages of BGA packages is their ability to accommodate a large number of interconnects. Unlike older packaging types that only use the edges for connections, BGA packages utilize the entire bottom surface. This allows for the integration of more complex ICs, enabling the development of smaller, more powerful electronic devices.
BGA packages also offer superior electrical and thermal performance. The short and uniform connections result in lower inductance, leading to improved electrical performance. The design of BGA packages also allows for better heat dissipation, enhancing the reliability of the device, especially at higher frequencies.
However, the use of BGA packages presents certain challenges. The manufacturing process requires precise placement and soldering, and the hidden solder joints make inspection and repair more difficult.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of BGA packages have led to their widespread adoption in the electronics industry. They are found in a variety of applications, from personal electronics like computers and smartphones to specialized equipment in the automotive and medical fields. Understanding the different types of BGA packages and their specific features is crucial for anyone involved in electronics design and manufacturing.
Types of BGA Packages
In my years of experience in the PCB & PCBA manufacturing industry, I’ve come across various types of BGA packages, each with its unique features and applications. Here’s a brief overview of the most common types:
| BGA Package Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBGA (Plastic Ball Grid Array) | Cost-effective, Easy to assemble, Good for low to moderate speed applications | Higher CTE, can lead to reliability issues in high-temperature environments | Consumer electronics, non-critical components |
| CBGA (Ceramic Ball Grid Array) | Excellent thermal and electrical performance, Lower CTE, Good for high-speed or high-power applications | More expensive, more complex assembly process | High-performance computing, telecommunications |
| FCBGA (Flip Chip Ball Grid Array) | High performance, high I/O density, Shorter signal path for faster data processing | More expensive, more complex assembly process | High-speed data processing, server applications |
| TBGA (Tape Ball Grid Array) | Good balance of performance, size, and cost, Thinner and lighter package | Higher CTE, can lead to reliability issues in high-temperature environments | Portable devices, applications with moderate performance requirements |
| µBGA (Micro Ball Grid Array) | Small size, high I/O density, Ideal for applications with tight space constraints | Small size can make assembly process more challenging, may require specialized equipment | Compact electronic devices, high-density mounting applications |
Plastic BGA (PBGA)
The Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA) is a type of BGA package that I’ve often seen in a wide range of applications. With a plastic body and an array of approximately 200 to 500 balls, this BGA type is versatile and cost-effective.
Ceramic BGA (CBGA)
The Ceramic BGA (CBGA) is another common type, especially in computer microprocessor chip technology. Its ceramic substrate and lower coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) make it a reliable choice for high-performance applications.
Tape BGA (TBGA)
When a thinner BGA solution is required, the Tape BGA (TBGA) package comes into play. It’s a slimmer alternative to conventional BGAs, ensuring optimal electrical and thermal performance.
Flip Chip BGA (FC-BGA)
In high-performance and high-density packaging applications, like high-speed processors and graphics cards, I’ve often recommended the Flip Chip BGA (FCBGA) packages. Their flip-chip technology allows for shorter interconnect lengths and higher speeds.
Metal BGA (MBGA)
For applications requiring enhanced electrical conduction properties, Metal BGAs (MBGAs) are a great choice. Their Copper/Polyimide substrate base material sets them apart from traditional BGAs.
Micro BGA
In the assembly of compact electronic devices like mobile devices and laptops, Micro BGA packages are often the go-to choice. Their small footprint and high-density mounting capabilities make them ideal for applications with limited space and high pin count requirements.
This overview provides a snapshot of the different types of BGA packages. However, to truly understand their impact on PCB & PCBA manufacturing, we need to delve deeper. In the following sections, we will explore each type in more detail, discussing their specific features, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
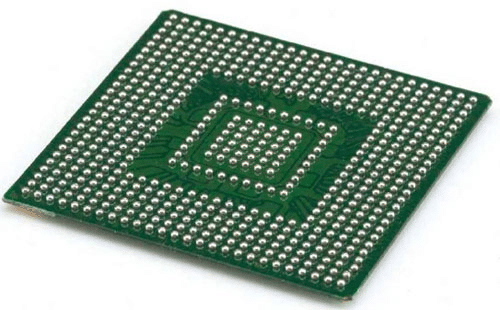
The Impact of BGA Packages on PCB & PCBA Manufacturing
When it comes to PCB & PCBA manufacturing, the choice of BGA packages can significantly influence your project’s success. But rather than getting lost in the technicalities, let’s focus on what matters most to you – how different BGA packages can affect your project’s performance, cost, and timeline.
- Performance
Different BGA packages offer varying levels of performance. For instance, Ceramic BGAs (CBGAs) and Flip Chip BGAs (FCBGAs) are known for their high-speed performance, making them ideal for projects that require fast data processing. On the other hand, Metal BGAs (MBGAs) offer enhanced electrical conduction properties, which can be crucial for projects that demand high electrical performance.
- Cost
The cost of BGA packages can vary widely. Plastic BGAs (PBGAs) are generally more cost-effective, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious projects. However, it’s important to remember that the initial cost of the package is just one part of the equation. The complexity of the assembly process and the potential need for rework can also affect the overall cost of your project.
- Timeline
The choice of BGA package can also impact your project timeline. Some BGA packages, like Tape BGAs (TBGAs), require a more complex assembly process, which can extend the production timeline. Conversely, simpler packages like PBGAs can often be assembled more quickly, helping to keep your project on schedule.
- Reliability
Reliability is a key concern in PCB & PCBA manufacturing. Packages like CBGAs and MBGAs, with their lower coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE), can offer improved reliability by reducing stress on solder joints during temperature changes. This can be a critical factor in ensuring the long-term success of your project.
- Size Constraints
For projects with tight space constraints, such as compact electronic devices, Micro BGA packages can be an excellent choice. Their small footprint and high-density mounting capabilities allow for the integration of more functionality in a smaller space, which can be a game-changer in today’s trend towards miniaturization in electronics.
Choosing the Right BGA Package for Your Needs
Selecting the right BGA package for your project is a critical decision that can significantly impact your product’s performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. It’s not just about picking the package with the most pins or the smallest size; it’s about finding the perfect fit for your specific needs. Here are some key considerations to guide your decision-making process:
Package Size and Integration Level
The size of the BGA package should align with the available space on your board and the level of integration you desire. For instance, if you’re designing a compact device like a smartwatch, a Micro BGA package with its small footprint could be an ideal choice. However, remember that a smaller package size often means a higher level of integration, which could complicate the PCB design and assembly process.
Pin Count and I/O Capabilities
The number of pins on the BGA package should match your application’s I/O requirements. More pins mean more I/O capabilities, but they also require a larger board footprint and more complex routing. For example, if your application involves complex computations and requires a high-speed processor, you might need a BGA package with a high pin count to accommodate the processor’s I/O needs.
Thermal and Electrical Performance
The BGA package you choose should have the thermal and electrical characteristics that match your IC and system requirements. For instance, if your application generates a lot of heat, you might want to consider a BGA package with excellent thermal conductivity, like a Ceramic BGA (CBGA) or a Metal BGA (MBGA). Similarly, if your application requires high-speed data processing, you might need a BGA package with superior electrical performance to maintain signal integrity and reduce noise.
Reliability and Durability
The reliability and durability of the BGA package are crucial, especially for applications that operate in harsh environments or undergo mechanical stress. Ceramic packages are generally more rugged and reliable than plastic packages. However, they are also more expensive. Therefore, you need to balance the reliability requirements with your project budget.
Cost Considerations
Last but not least, cost is a significant factor in choosing a BGA package. While it might be tempting to go for the cheapest option, remember that the initial cost of the package is just one part of the equation. You also need to consider the assembly costs, the potential need for rework, and the lifecycle costs, including maintenance and repair.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of BGA packages is no small task, but understanding their differences and implications is crucial to the success of your PCB & PCBA projects. The right BGA package can enhance performance, ensure reliability, and optimize costs, making it a pivotal decision in the manufacturing process.
At Rowsum, we understand the importance of this strategic decision and are committed to providing the expertise and support you need. Our comprehensive suite of services, including PCB manufacturing, PCB assembly, and components sourcing, are designed to meet your project’s unique needs.
We’re more than just a service provider – we’re a partner in your journey to success. For more information or to discuss your project’s needs, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at [email protected]. Let Rowsum be your trusted partner in navigating the complexities of BGA packages and ensuring the success of your PCB & PCBA projects.